What is sustainability? Sustainability vs CSR vs ESG
- Anna Neumann
- May 5, 2023
- 3 min read

In the current business world sustainability is no longer a fancy word, but more and more a requirement. One-sided annual financial reports are now more frequently accompanied by the Report of the Non-Financial or Sustainability indicators. While financial reporting shows the company current health and state, Non-Financial or Sustainability indicators show its future.
According to KPMG 96% of the 250 world leading companies report on sustainability. Cone Communications CSR Study reveals that 87 % of customers will purchase a product, because of the company is engaged in relevant for the customers topic/sustainability issues and will refuse to buy a product if the company actions do not correspond with their beliefs.
However, terminology of sustainability may be unclear. CSR and ESG are also being often used as synonyms of sustainability.
What is the difference between sustainability, CSR & ESG?
Sustainability
United Nations Brundtland Commission provides the following definition: sustainability is “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.“ Sustainability could be seen as an overarching term including both CSR & ESG approaches and addressing fair and just resources use and human interactions. There is no set number of agreed indicators for measuring sustainability, however, It could be to some extend measured through ESG indicators. 3 pillars comprising sustainability (also called “triple bottom line of sustainability”) are: social, environmental and economic. Often social part is specifically defined as human and governance aspects. United Nations provide good visual representation of these 3 pillars:

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Concept of Corporate and Social responsibility was introduced by American economist Howard Bowen in 1953. It started as a voluntarily movement for businesses to donate to charity and provide better working conditions to employees. Now it has developed to an area with wide range of actions in social, environmental and economic areas. CSR represents a company internal values and culture and should be embedded in all company policies. It is now becoming a demand from the employees and customers perspective.
Few good global examples of CSR initiatives:
-improving working conditions and related policies
-improving inclusion and employee rights protection
-participating in organic and fair-trade initiatives and certifications
-reducing its environmental and carbon footprint
-giving back to community though volunteering and donations
Environment, Social, Governance (ESG)
ESG is also focused on the same 3 pillars of sustainability, but focus lies with on quantitative data assessment related to measuring of the 3 pillars aspects. Additional emphasis lies on company governance. It is popular with investors and external stakeholders and used as a way to provide a quantitative proof of company sustainability aspirations and achievements. It measures, social & environmental indicators and shows its impact on financial health and future of the organization. ESG was introduced by United Nations Environment Programme Initiative in 2005 and since than gained more popularity than CSR due to its quantifiable, measurable nature. Good ESG performance reduces capital costs and improves company valuation, increasing availability of funding. Therefore, ESG area could be often placed in a company compliance and audit departments.
Examples of most common ESG indicators:
-energy efficiency
-Green House Gas emissions
-staff turnover
-staff age distribution and diversity
-staff training and qualification
-corruption & tax transparency etc.
Here are most common ESG areas identified by PWC:
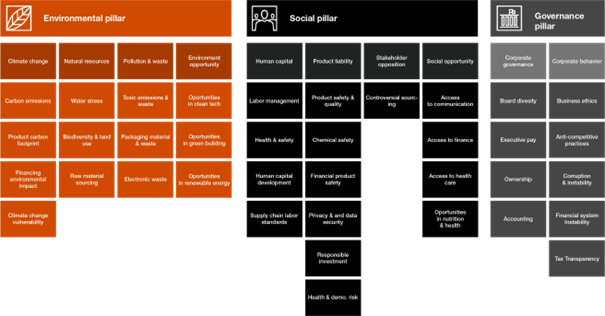
CSR vs. ESG Comparison
1. CSR is usually voluntarily and self-regulated. ESG – often external compliance required by investors and other stakeholders
2. CSR – mostly impacts organizational internal culture and policies. ESG focuses on external impact of company on a social and natural environment.
3. CSR – qualitative goals (values & strategy). ESG - measurable quantitative indicators (materiality analysis, KPIs, cost-saving)
4. CSR – mostly relevant for employees and customers; ESG -. Important for investors and stakeholders and measures long-term progress
5. CSR – oriented towards company values. ESG – oriented towards materiality and financial business stability
6. CSR – can have a broader scope, ESG – focuses on the indicators and report scope
7. CSR – approaches and reporting can vary from company to company; ESG – more standardized reports.
Reach out to Greenativity for initial analysis and step by step solutions for your business sustainability!


Comentários